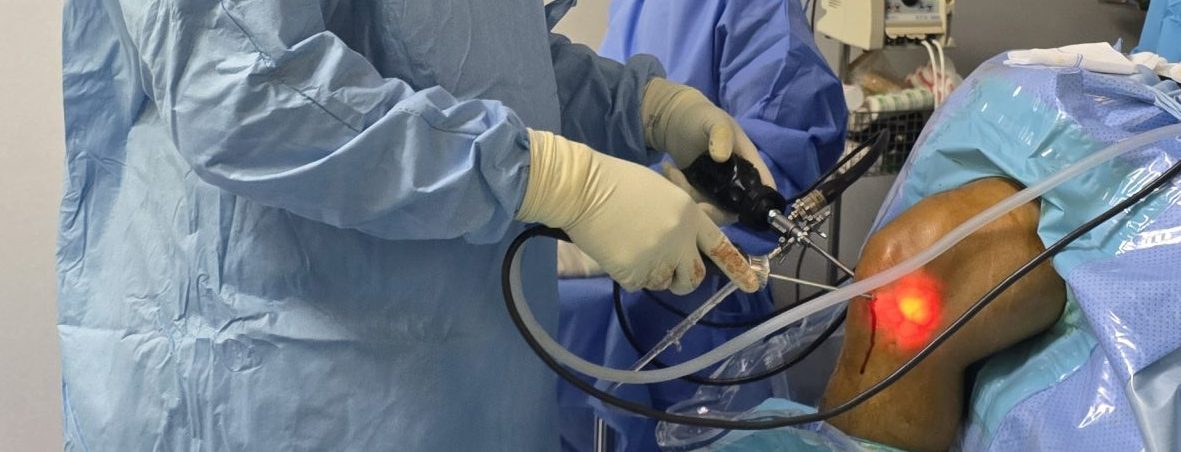
Understanding Injuries, Treatments, and History of Orthopedics
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
 Orthopaedic injuries are a common occurrence globally, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds.
Orthopaedic injuries are a common occurrence globally, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds.
Whether through sports activities, workplace accidents, or everyday mishaps, musculoskeletal injuries can significantly impact one’s quality of life.
From minor strains to complex fractures, orthopedic conditions require specialized care to ensure proper diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation.
What are Orthopedic Injuries?
Orthopedics, derived from the Greek words “ortho” (straight) and “paideia” (child), initially focused on correcting musculoskeletal deformities in children.
Over time, it evolved into a comprehensive medical specialty dedicated to the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system.
This system comprises bones, muscles, joints, ligaments, tendons, and nerves, all vital for movement, stability, and overall function.
Orthopedic specialists, also known as orthopedic surgeons or orthopedists, undergo extensive training to address a broad spectrum of musculoskeletal conditions.
From acute sports injuries to chronic degenerative diseases like osteoarthritis, orthopedic surgeons play a crucial role in managing various orthopedic disorders.
They collaborate closely with other healthcare professionals, including physical therapists and rehabilitation specialists, to provide comprehensive care tailored to each patient’s needs.
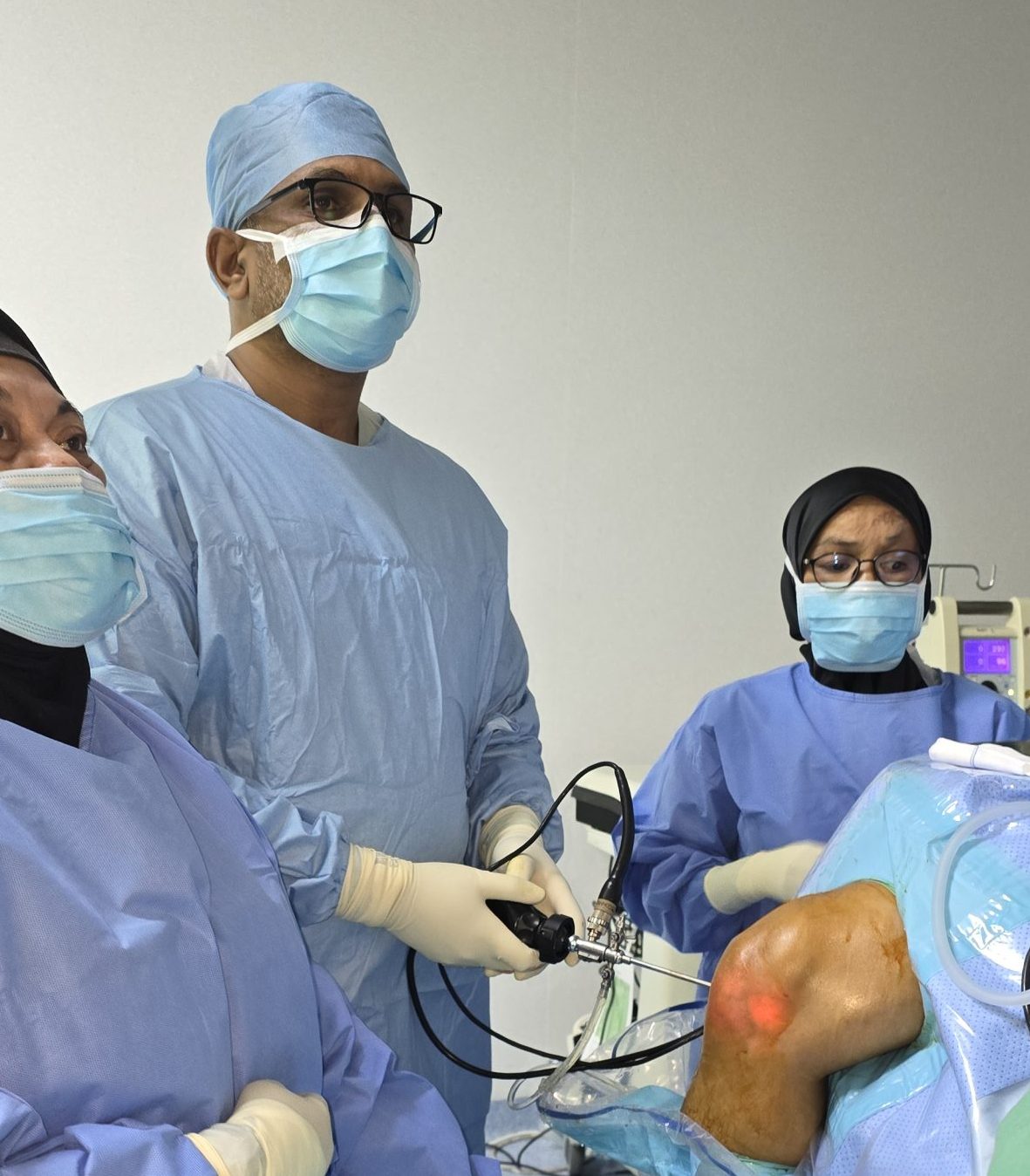 Orthopedic Injuries in Malaysia
Orthopedic Injuries in Malaysia
In Malaysia, the practice of orthopedics has a rich history intertwined with the country’s development of modern medicine.
From its colonial past to the present day, Malaysia has witnessed significant advancements in orthopedic care, with the establishment of specialized hospitals and training programs for orthopedic surgeons.
Orthopedic surgery in Malaysia traces its origins back to the colonial era when British physicians introduced modern medical practices to the region.
Since then, local orthopedic surgeons have contributed to the growth of the field, adapting international standards to meet Malaysia’s diverse healthcare needs.
Globally, the history of orthopedics spans millennia, with ancient civilizations employing various techniques to treat musculoskeletal injuries.
From the ancient Egyptian “Edwin Smith Papyrus” to the Hippocratic Corpus of ancient Greece, early medical texts contain descriptions of orthopedic conditions and their treatments, reflecting humanity’s enduring quest to understand and manage musculoskeletal disorders.
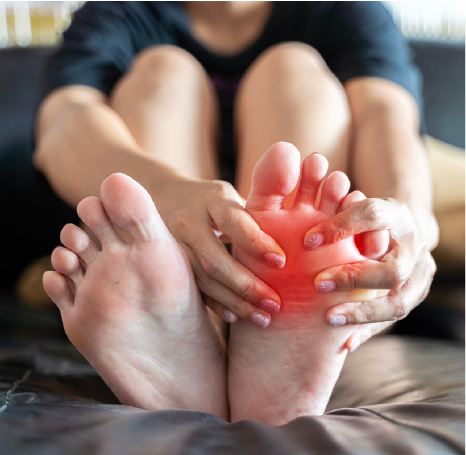 Definition, Risk Factors, and Symptoms in Orthopedic Injuries
Definition, Risk Factors, and Symptoms in Orthopedic Injuries
Orthopedic conditions encompass a wide range of disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system, each with its own set of risk factors, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
Common orthopedic disorders include fractures, sprains, strains, arthritis, tendonitis, and spinal disorders.
Risk factors for orthopedic conditions can vary significantly depending on the specific disorder.
For example, participation in high-impact sports or physical activities increases the risk of sports-related injuries such as ligament tears or fractures.
Poor posture or biomechanics may contribute to conditions like chronic back pain or repetitive strain injuries.
Additionally, genetic factors, obesity, and occupational hazards can also influence orthopedic health.
Symptoms of orthopedic conditions can manifest in various ways, often depending on the underlying cause.
For instance, fractures typically present with localized pain, swelling, and deformity, whereas arthritis may cause joint stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion.
Prompt diagnosis of orthopedic conditions is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and preventing complications.
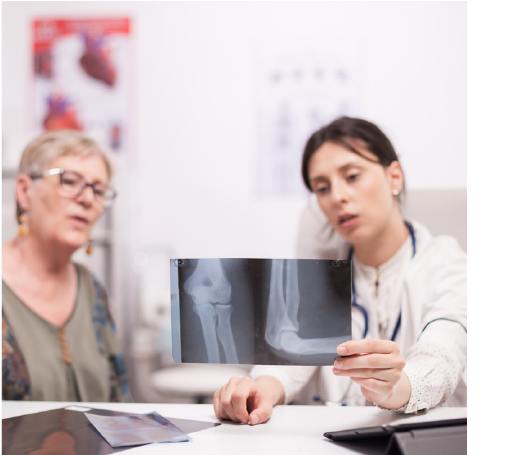 Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of orthopedic injury typically involves a multifaceted approach, including:
- Medical history: Gathering information about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and any previous injuries or treatments.
- Physical examination: Assessing the affected area for signs of inflammation, instability, or deformity.
- Imaging studies: Utilizing X-rays, MRI, CT scans, or ultrasound to visualize the bones, joints, and soft tissues for abnormalities.
- Blood investigations: Doing a blood workup to diagnose certain conditions such as Gouty arthritis or Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Diagnostic procedures: Performing specialized tests such as arthroscopy, bone scans, or electromyography to further evaluate the condition.
Treatment approaches for orthopedic conditions are tailored to each patient’s specific diagnosis, severity of symptoms, and individual needs. Conservative treatments may include:
- Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE): Initial management for acute injuries to reduce pain and inflammation.
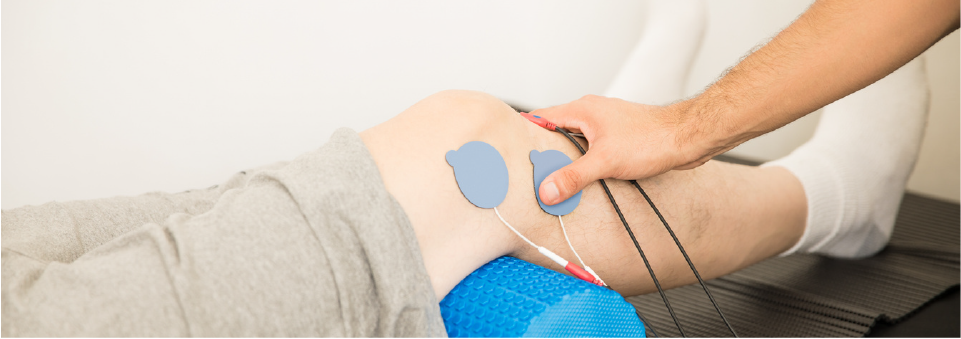
- Physical therapy or exercise rehabilitation: Strengthening exercises, stretching, and manual therapy to improve joint function and mobility.
- Pain management: Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroid injections, or analgesics to alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Orthopedic devices: Braces, splints, or orthotics to support injured joints or correct biomechanical issues.
In cases where conservative measures are ineffective or the condition is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Orthopedic surgeries range from minimally invasive procedures like arthroscopy to complex reconstructions such as joint replacement or spinal fusion.
The goal of surgical treatment is to restore function, alleviate pain, and improve the patient’s quality of life.
In addition to formal education and training, successful orthopedic surgeons possess essential qualities such as excellent hand-eye coordination, attention to detail, problem-solving skills, and effective communication abilities.
They must also stay abreast of advances in orthopedic research, surgical techniques, and medical technology to provide the highest standard of care to their patients.
In Conclusion
Orthopedics is a multifaceted medical specialty dedicated to the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders.
From historical origins to modern-day advancements, orthopedic care continues to evolve, driven by innovation, research, and the commitment of orthopedic professionals worldwide.
By understanding the principles of orthopedics and the qualifications necessary to become an orthopedist, individuals can appreciate the complexity of this field and the critical role it plays in restoring mobility, function, and quality of life for patients.